Workflow settings
Workflow settings
The workflow settings specify when the work is started and when it's completed. It is used in calculating metrics such as lead or cycle time of issues and pull requests.
The workflow settings specify when the work is started and when it's completed. It is used in calculating metrics such as lead or cycle time of issues and pull requests.
The workflow settings specify when the work is started and when it's completed. It is used in calculating metrics such as lead or cycle time of issues and pull requests.
Guide contents:
Guide contents:
Map your GitHub worklow
When importing a GitHub Project as a data source, your board columns are automatically mapped to either Not started, In progress, or Done. This information is used when calculating the Timing metrics.

If the suggested mapping looks correct, you can accept it by clicking Looks good to me. To make changes, click Adjust mapping. The boxes become editable, and you can drag & drop items between them.
Not started = Work to be done
In progress = Work started but not completed
Done = Completed work
Consider your work done only when tasks are fully done, so map your testing/review/waiting states to In progress rather than Done. That provides you with a better picture of your cycle times, including all the reviews that need to be done before a task is complete.
When importing repositories (instead of Projects), the timing metrics are calculated as below:
Lead time starts when an issue is created
Cycle time starts when the issue is assigned to a person, or when pull request is opened
Lead & cycle time is stopped when the issue is closed, or the pull request merged
Map your GitHub worklow
When importing a GitHub Project as a data source, your board columns are automatically mapped to either Not started, In progress, or Done. This information is used when calculating the Timing metrics.

If the suggested mapping looks correct, you can accept it by clicking Looks good to me. To make changes, click Adjust mapping. The boxes become editable, and you can drag & drop items between them.
Not started = Work to be done
In progress = Work started but not completed
Done = Completed work
Consider your work done only when tasks are fully done, so map your testing/review/waiting states to In progress rather than Done. That provides you with a better picture of your cycle times, including all the reviews that need to be done before a task is complete.
When importing repositories (instead of Projects), the timing metrics are calculated as below:
Lead time starts when an issue is created
Cycle time starts when the issue is assigned to a person, or when pull request is opened
Lead & cycle time is stopped when the issue is closed, or the pull request merged
Accessing the workflow settings
You can access the workflow settings by selecting Data Mapping from the main menu.

When using GitHub projects, you may add new columns to your board. By default, new workflow states are automatically mapped to either Not started, In progress, or Done. Alternatively, you can force the mapping of new states by selecting one of the other options from the menu.

Accessing the workflow settings
You can access the workflow settings by selecting Data Mapping from the main menu.

When using GitHub projects, you may add new columns to your board. By default, new workflow states are automatically mapped to either Not started, In progress, or Done. Alternatively, you can force the mapping of new states by selecting one of the other options from the menu.

Learn more
Learn more
FAQ
Common questions
It depends on whether you're importing GitHub repositories or GitHub Projects.
When you import GitHub repositories, one data source can contain multiple repositories. You can select the repositories to include in the data source by selecting them at the time of import.
When you import GitHub Projects, a data source is one GitHub Project.
The difference between these is that when importing a GitHub Project, you can use project metadata, such as statuses, iterations, and custom fields, in your reports, which are not available when importing repositories.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
It depends on whether you're importing GitHub repositories or GitHub Projects.
When you import GitHub repositories, one data source can contain multiple repositories. You can select the repositories to include in the data source by selecting them at the time of import.
When you import GitHub Projects, a data source is one GitHub Project.
The difference between these is that when importing a GitHub Project, you can use project metadata, such as statuses, iterations, and custom fields, in your reports, which are not available when importing repositories.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
Yes, we support both user-owned and organization-wide project boards as well as repository project boards. You can import both classic and new projects.
Yes, we support both user-owned and organization-wide project boards as well as repository project boards. You can import both classic and new projects.
When you import a data source, all data is imported and made available for reporting. You can narrow the data to any subset by setting a filter. For example, you can filter out issues or pull request by using 'Type' filter.
When you import a data source, all data is imported and made available for reporting. You can narrow the data to any subset by setting a filter. For example, you can filter out issues or pull request by using 'Type' filter.
You can track pull request review times by adding Pull request review time as a column in a Task list. The summary on the bottom shows the sum, average, or median time to review a pull request. You can learn more from this guide.
You can track pull request review times by adding Pull request review time as a column in a Task list. The summary on the bottom shows the sum, average, or median time to review a pull request. You can learn more from this guide.
The Analytics & Reports GitHub App requires read-only access to issues, members, metadata, organization administration, organization projects, pull requests, and repository projects.
The Analytics & Reports GitHub App requires read-only access to issues, members, metadata, organization administration, organization projects, pull requests, and repository projects.
The Analytics & Reports OAuth app requires these OAuth scopes:
"read:org"
"repo" or "public_repo" (depending on whether user selects "authorise public repos only" or "authorize public and private repos”
An OAuth token will share the permissions of the user that authorized the application. That means, if your account authorizes the application and has 'write' permission to a repository, the token will also have 'write' permission to that repository. This is how OAuth tokens work in the GitHub platform.
From a security point of view, we recommend using the GitHub app instead of the OAuth app.
The Analytics & Reports OAuth app requires these OAuth scopes:
"read:org"
"repo" or "public_repo" (depending on whether user selects "authorise public repos only" or "authorize public and private repos”
An OAuth token will share the permissions of the user that authorized the application. That means, if your account authorizes the application and has 'write' permission to a repository, the token will also have 'write' permission to that repository. This is how OAuth tokens work in the GitHub platform.
From a security point of view, we recommend using the GitHub app instead of the OAuth app.
You can’t switch an existing Screenful account from OAuth to GitHub App. To use the GitHub App, you need to create a new Screenful account.
You can’t switch an existing Screenful account from OAuth to GitHub App. To use the GitHub App, you need to create a new Screenful account.
When importing project boards, you can specify your workflow based on the columns on the board which you can configure in the workflow settings. You can learn more from the Lead Time FAQ.
When importing repositories, the timing metrics are calculated as follows:
Lead time starts when an issue is created
Cycle time starts when the issue is assigned to a person, or when pull request is opened
Lead & cycle time is stopped when the issue is closed, or the pull request merged
When importing project boards, you can specify your workflow based on the columns on the board which you can configure in the workflow settings. You can learn more from the Lead Time FAQ.
When importing repositories, the timing metrics are calculated as follows:
Lead time starts when an issue is created
Cycle time starts when the issue is assigned to a person, or when pull request is opened
Lead & cycle time is stopped when the issue is closed, or the pull request merged
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Does this support my specific workflow or do I have to use some specific states like "open", "in progress" and "done"?
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
FAQ
Common questions
It depends on whether you're importing GitHub repositories or GitHub Projects.
When you import GitHub repositories, one data source can contain multiple repositories. You can select the repositories to include in the data source by selecting them at the time of import.
When you import GitHub Projects, a data source is one GitHub Project.
The difference between these is that when importing a GitHub Project, you can use project metadata, such as statuses, iterations, and custom fields, in your reports, which are not available when importing repositories.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
It depends on whether you're importing GitHub repositories or GitHub Projects.
When you import GitHub repositories, one data source can contain multiple repositories. You can select the repositories to include in the data source by selecting them at the time of import.
When you import GitHub Projects, a data source is one GitHub Project.
The difference between these is that when importing a GitHub Project, you can use project metadata, such as statuses, iterations, and custom fields, in your reports, which are not available when importing repositories.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
Yes, we support both user-owned and organization-wide project boards as well as repository project boards. You can import both classic and new projects.
Yes, we support both user-owned and organization-wide project boards as well as repository project boards. You can import both classic and new projects.
When you import a data source, all data is imported and made available for reporting. You can narrow the data to any subset by setting a filter. For example, you can filter out issues or pull request by using 'Type' filter.
When you import a data source, all data is imported and made available for reporting. You can narrow the data to any subset by setting a filter. For example, you can filter out issues or pull request by using 'Type' filter.
You can track pull request review times by adding Pull request review time as a column in a Task list. The summary on the bottom shows the sum, average, or median time to review a pull request. You can learn more from this guide.
You can track pull request review times by adding Pull request review time as a column in a Task list. The summary on the bottom shows the sum, average, or median time to review a pull request. You can learn more from this guide.
The Analytics & Reports GitHub App requires read-only access to issues, members, metadata, organization administration, organization projects, pull requests, and repository projects.
The Analytics & Reports GitHub App requires read-only access to issues, members, metadata, organization administration, organization projects, pull requests, and repository projects.
The Analytics & Reports OAuth app requires these OAuth scopes:
"read:org"
"repo" or "public_repo" (depending on whether user selects "authorise public repos only" or "authorize public and private repos”
An OAuth token will share the permissions of the user that authorized the application. That means, if your account authorizes the application and has 'write' permission to a repository, the token will also have 'write' permission to that repository. This is how OAuth tokens work in the GitHub platform.
From a security point of view, we recommend using the GitHub app instead of the OAuth app.
The Analytics & Reports OAuth app requires these OAuth scopes:
"read:org"
"repo" or "public_repo" (depending on whether user selects "authorise public repos only" or "authorize public and private repos”
An OAuth token will share the permissions of the user that authorized the application. That means, if your account authorizes the application and has 'write' permission to a repository, the token will also have 'write' permission to that repository. This is how OAuth tokens work in the GitHub platform.
From a security point of view, we recommend using the GitHub app instead of the OAuth app.
You can’t switch an existing Screenful account from OAuth to GitHub App. To use the GitHub App, you need to create a new Screenful account.
You can’t switch an existing Screenful account from OAuth to GitHub App. To use the GitHub App, you need to create a new Screenful account.
When importing project boards, you can specify your workflow based on the columns on the board which you can configure in the workflow settings. You can learn more from the Lead Time FAQ.
When importing repositories, the timing metrics are calculated as follows:
Lead time starts when an issue is created
Cycle time starts when the issue is assigned to a person, or when pull request is opened
Lead & cycle time is stopped when the issue is closed, or the pull request merged
When importing project boards, you can specify your workflow based on the columns on the board which you can configure in the workflow settings. You can learn more from the Lead Time FAQ.
When importing repositories, the timing metrics are calculated as follows:
Lead time starts when an issue is created
Cycle time starts when the issue is assigned to a person, or when pull request is opened
Lead & cycle time is stopped when the issue is closed, or the pull request merged
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Does this support my specific workflow or do I have to use some specific states like "open", "in progress" and "done"?
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
FAQ
Troubleshooting
You can pull metrics from repositories that you own or that are in your organisation. If your organisation has applied special restrictions on 3rd party access you need to grant access to the Screenful app first.
You can pull metrics from repositories that you own or that are in your organisation. If your organisation has applied special restrictions on 3rd party access you need to grant access to the Screenful app first.
When you create a new Organization within GitHub it may not automatically appear within Screenful. You may need to enable access to the new organizaion within the GItHub UI.
Notice also that the OAuth integration is managed per user account rather than per organization. The integration will see all the organizations for that GitHub user.
To add your new GitHub organization, you will need to add access to Screenful for this new organization:
Navigate to Account(top right) > Settings > Applications > Authorized OAuth Apps
Click on Screenful
Find your Organization(s) and click on Grant.
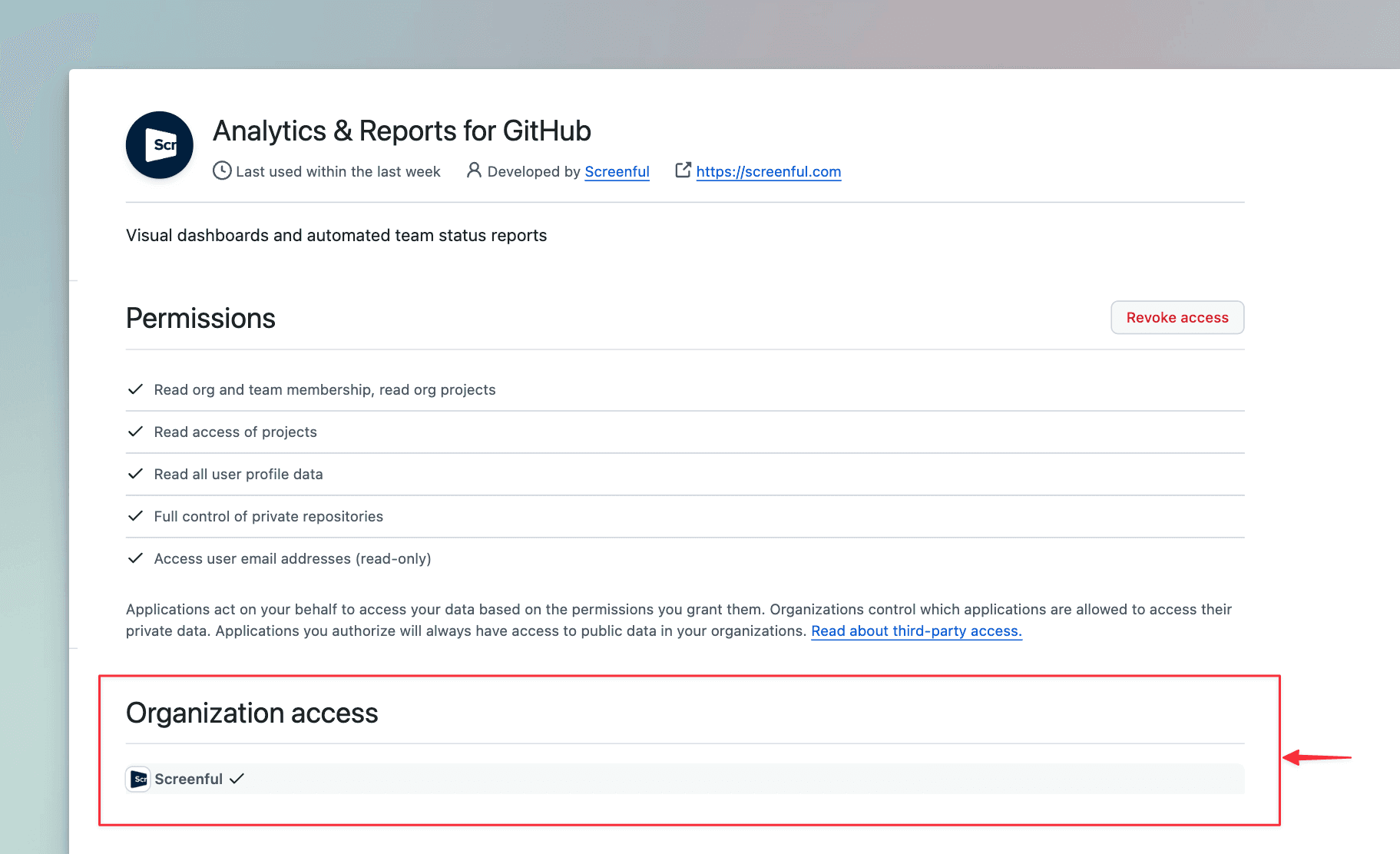
You should now be able to import repositories and projects from this organization!
When you create a new Organization within GitHub it may not automatically appear within Screenful. You may need to enable access to the new organizaion within the GItHub UI.
Notice also that the OAuth integration is managed per user account rather than per organization. The integration will see all the organizations for that GitHub user.
To add your new GitHub organization, you will need to add access to Screenful for this new organization:
Navigate to Account(top right) > Settings > Applications > Authorized OAuth Apps
Click on Screenful
Find your Organization(s) and click on Grant.

You should now be able to import repositories and projects from this organization!
Go to the Applications settings in GitHub and remove Screenful from the authorised OAuth applications. After that, you can import projects or repositories using a different GitHub account.
Go to the Applications settings in GitHub and remove Screenful from the authorised OAuth applications. After that, you can import projects or repositories using a different GitHub account.
Pull request reviewer means a person, team, or bot that has been requested to review a pull request, regardless of whether the reviewer has taken any action. The pull request review time can be zero in the following cases:
Pull request hasn't been merged
Review took place after the pull request was merged
Review was never requested (in which case the review time is zero because the counting starts from the moment the pull review was requested)
Pull request reviewer means a person, team, or bot that has been requested to review a pull request, regardless of whether the reviewer has taken any action. The pull request review time can be zero in the following cases:
Pull request hasn't been merged
Review took place after the pull request was merged
Review was never requested (in which case the review time is zero because the counting starts from the moment the pull review was requested)
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.
FAQ
Troubleshooting
You can pull metrics from repositories that you own or that are in your organisation. If your organisation has applied special restrictions on 3rd party access you need to grant access to the Screenful app first.
You can pull metrics from repositories that you own or that are in your organisation. If your organisation has applied special restrictions on 3rd party access you need to grant access to the Screenful app first.
When you create a new Organization within GitHub it may not automatically appear within Screenful. You may need to enable access to the new organizaion within the GItHub UI.
Notice also that the OAuth integration is managed per user account rather than per organization. The integration will see all the organizations for that GitHub user.
To add your new GitHub organization, you will need to add access to Screenful for this new organization:
Navigate to Account(top right) > Settings > Applications > Authorized OAuth Apps
Click on Screenful
Find your Organization(s) and click on Grant.

You should now be able to import repositories and projects from this organization!
When you create a new Organization within GitHub it may not automatically appear within Screenful. You may need to enable access to the new organizaion within the GItHub UI.
Notice also that the OAuth integration is managed per user account rather than per organization. The integration will see all the organizations for that GitHub user.
To add your new GitHub organization, you will need to add access to Screenful for this new organization:
Navigate to Account(top right) > Settings > Applications > Authorized OAuth Apps
Click on Screenful
Find your Organization(s) and click on Grant.

You should now be able to import repositories and projects from this organization!
Go to the Applications settings in GitHub and remove Screenful from the authorised OAuth applications. After that, you can import projects or repositories using a different GitHub account.
Go to the Applications settings in GitHub and remove Screenful from the authorised OAuth applications. After that, you can import projects or repositories using a different GitHub account.
Pull request reviewer means a person, team, or bot that has been requested to review a pull request, regardless of whether the reviewer has taken any action. The pull request review time can be zero in the following cases:
Pull request hasn't been merged
Review took place after the pull request was merged
Review was never requested (in which case the review time is zero because the counting starts from the moment the pull review was requested)
Pull request reviewer means a person, team, or bot that has been requested to review a pull request, regardless of whether the reviewer has taken any action. The pull request review time can be zero in the following cases:
Pull request hasn't been merged
Review took place after the pull request was merged
Review was never requested (in which case the review time is zero because the counting starts from the moment the pull review was requested)
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.