Set a filter for a chart
Set a filter for a chart
Want to filter the contents of charts? We've got you covered since you can filter charts by any available property such as assignee or label. You can also filter by your custom fields. This guide teaches you how to use filters like a pro!
Want to filter the contents of charts? We've got you covered since you can filter charts by any available property such as assignee or label. You can also filter by your custom fields. This guide teaches you how to use filters like a pro!
Want to filter the contents of charts? We've got you covered since you can filter charts by any available property such as assignee or label. You can also filter by your custom fields. This guide teaches you how to use filters like a pro!
Guide contents:
Guide contents:
How to find the filter feature?
Each chart has its own filter. Therefore, to filter the contents of a report, you need to open an individual chart for editing, and then adjust the filter by clicking Set filter in the chart editor:

When you are editing a report under the Reports tab, you access the filter of an individual chart by clicking the Edit chart icon next to the three dots menu:

When you are in the Insights tab, you can filter all the charts at once by clicking the Set filter button on the top toolbar:

Note that when you set a filter in the Insights tab, it only affects what you see. Other users have their own filter.
When you click the Set filter button in any of those views, the same filter modal is shown:

In the filter modal, you can set filters such as label include “bug” or label does not include “bug”. You can also do more complex filters involving number comparisons, date comparisons, etc.
If you add new custom fields to your board, they will be automatically imported and made available for filters after the next data sync (data is synced once per hour). You can trigger sync manually at the integration settings.
How to find the filter feature?
Each chart has its own filter. Therefore, to filter the contents of a report, you need to open an individual chart for editing, and then adjust the filter by clicking Set filter in the chart editor:

When you are editing a report under the Reports tab, you access the filter of an individual chart by clicking the Edit chart icon next to the three dots menu:

When you are in the Insights tab, you can filter all the charts at once by clicking the Set filter button on the top toolbar:

Note that when you set a filter in the Insights tab, it only affects what you see. Other users have their own filter.
When you click the Set filter button in any of those views, the same filter modal is shown:

In the filter modal, you can set filters such as label include “bug” or label does not include “bug”. You can also do more complex filters involving number comparisons, date comparisons, etc.
If you add new custom fields to your board, they will be automatically imported and made available for filters after the next data sync (data is synced once per hour). You can trigger sync manually at the integration settings.
Filtering by assignee, label, board, project, etc.
You can filter by any of the task properties available in your data such as assignee, group, label, board, project, sprint, milestone etc.
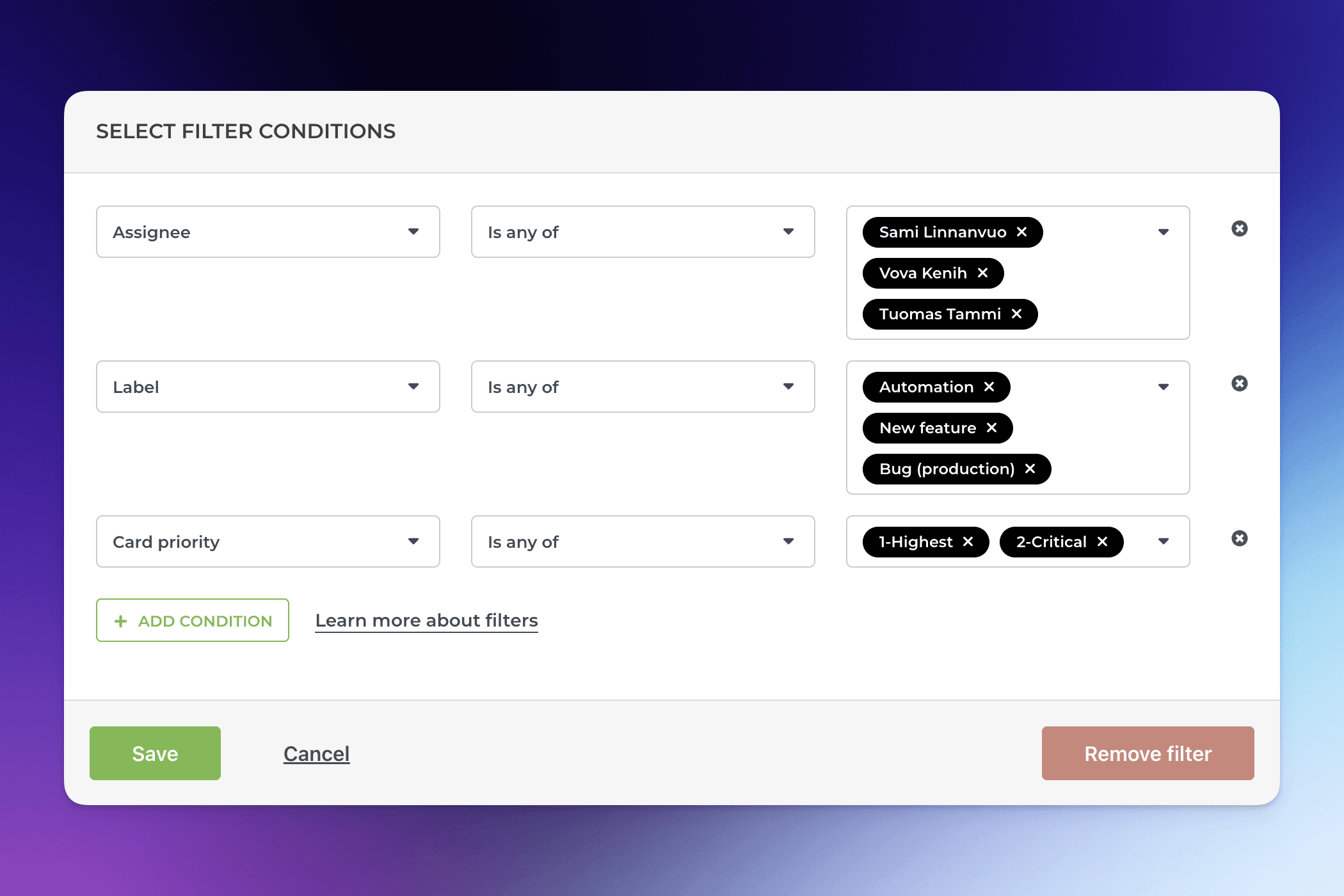
The available filters depend on the data source. The common filter for all data sources include assignee, label/tag, data source, workflow state, and mapped state. Depending on the data source, you can also filter by project, section, group, sprint, epic, milestone, version etc.
You can set multiple filters by selecting them one by one. Each filter can have multiple options for is any of or is none of.
Once you have set the filters, click Save to apply the filter to the chart.
Filtering by assignee, label, board, project, etc.
You can filter by any of the task properties available in your data such as assignee, group, label, board, project, sprint, milestone etc.

The available filters depend on the data source. The common filter for all data sources include assignee, label/tag, data source, workflow state, and mapped state. Depending on the data source, you can also filter by project, section, group, sprint, epic, milestone, version etc.
You can set multiple filters by selecting them one by one. Each filter can have multiple options for is any of or is none of.
Once you have set the filters, click Save to apply the filter to the chart.
Filtering by number fields
You can filter charts by any of your number fields. You can find them in the filter options, and you can do comparisons such as is greater than or is less than:

You can also filter by exact match using is equal to or is not equal to:

You can also filter by which items have a value or do not have a value by selecting is empty or is not empty:

Filtering by number fields
You can filter charts by any of your number fields. You can find them in the filter options, and you can do comparisons such as is greater than or is less than:

You can also filter by exact match using is equal to or is not equal to:

You can also filter by which items have a value or do not have a value by selecting is empty or is not empty:

Filtering by date fields
You can filter a chart by any of your date fields. When you select a date field in the filter, you can select within the last, not within the last, within the next or not within the next and enter the number of days:

In the above example, the filter will include items items with Date created within the last 10 days.
Alternatively, you can select before or after, and use the date picker to select the date:
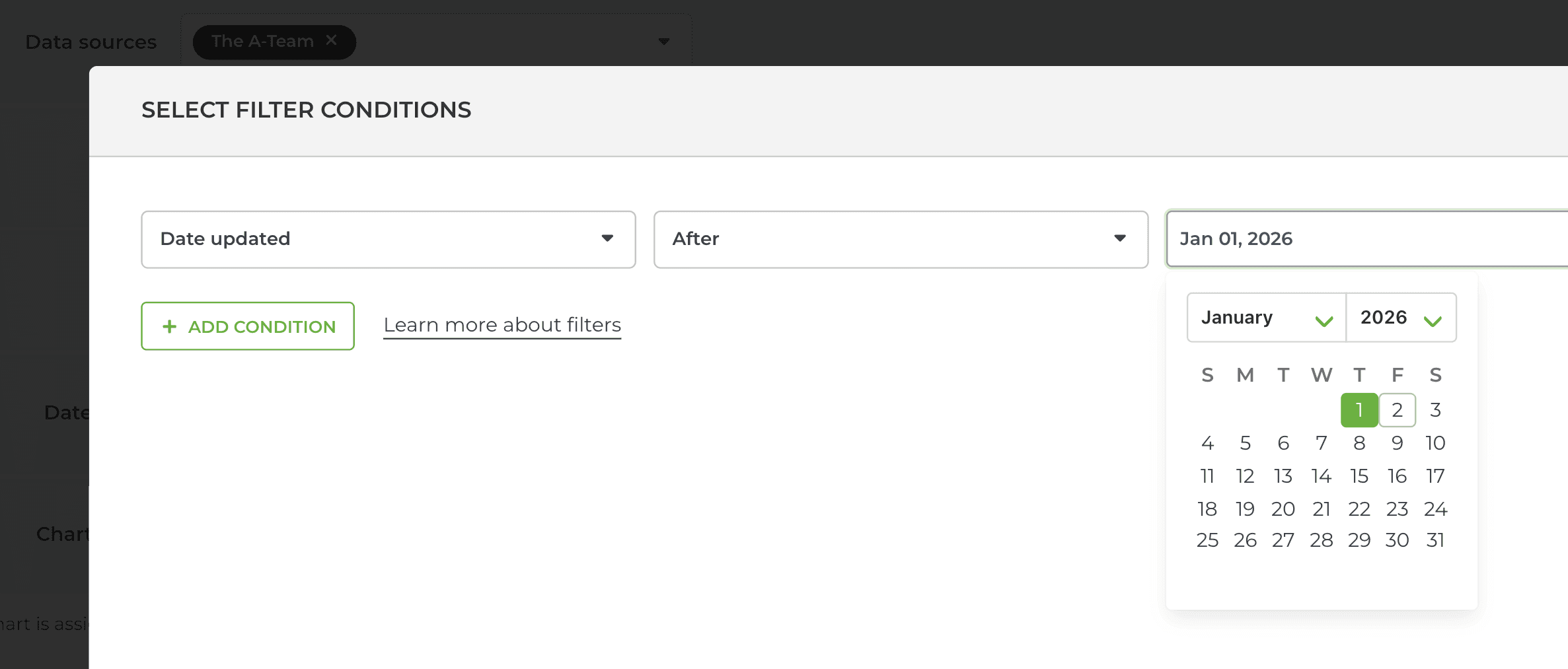
That will select all items with Date updated after the selected date. You use any of your date fields in the filter, including any of your custom date fields.
Filtering by date fields
You can filter a chart by any of your date fields. When you select a date field in the filter, you can select within the last, not within the last, within the next or not within the next and enter the number of days:

In the above example, the filter will include items items with Date created within the last 10 days.
Alternatively, you can select before or after, and use the date picker to select the date:

That will select all items with Date updated after the selected date. You use any of your date fields in the filter, including any of your custom date fields.
Filtering by text fields
You can add any of your text fields as columns to the Taks list. However, a lesser-known fact is that you can also use them for grouping and filtering data.

Before you can use your custom text fields in grouping and filtering, you need to map them as Group & filter first.
Filtering by text fields
You can add any of your text fields as columns to the Taks list. However, a lesser-known fact is that you can also use them for grouping and filtering data.

Before you can use your custom text fields in grouping and filtering, you need to map them as Group & filter first.
Filtering by substring
You can filter by partial text match using Contains or Doesn't contain. You can type the phrase in the filter window. It will be matched against the selected field, such as Label:

Selecting Label Contains "Bug", filters all the items that have the characters "Bug" as part of the label name. That would include labels susch as "Bug production" and "Bug staging".
Filtering by substring
You can filter by partial text match using Contains or Doesn't contain. You can type the phrase in the filter window. It will be matched against the selected field, such as Label:

Selecting Label Contains "Bug", filters all the items that have the characters "Bug" as part of the label name. That would include labels susch as "Bug production" and "Bug staging".
Filtering by task name
You can filter by the name of the item (issue/task/story, etc.) by selecting Item name from the filter menu.

You can enter the full name of the item, or use a substring of the name to include or exclude specific items from the set.
Filtering by task name
You can filter by the name of the item (issue/task/story, etc.) by selecting Item name from the filter menu.

You can enter the full name of the item, or use a substring of the name to include or exclude specific items from the set.
Filtering by timings
You can filter by timings such as total time in progress (cycle time), time in a workflow state, or time logged to a time tracking field.
To find items that have been in progress for longer than a certain number of days, select Time in progress from the filter menu:
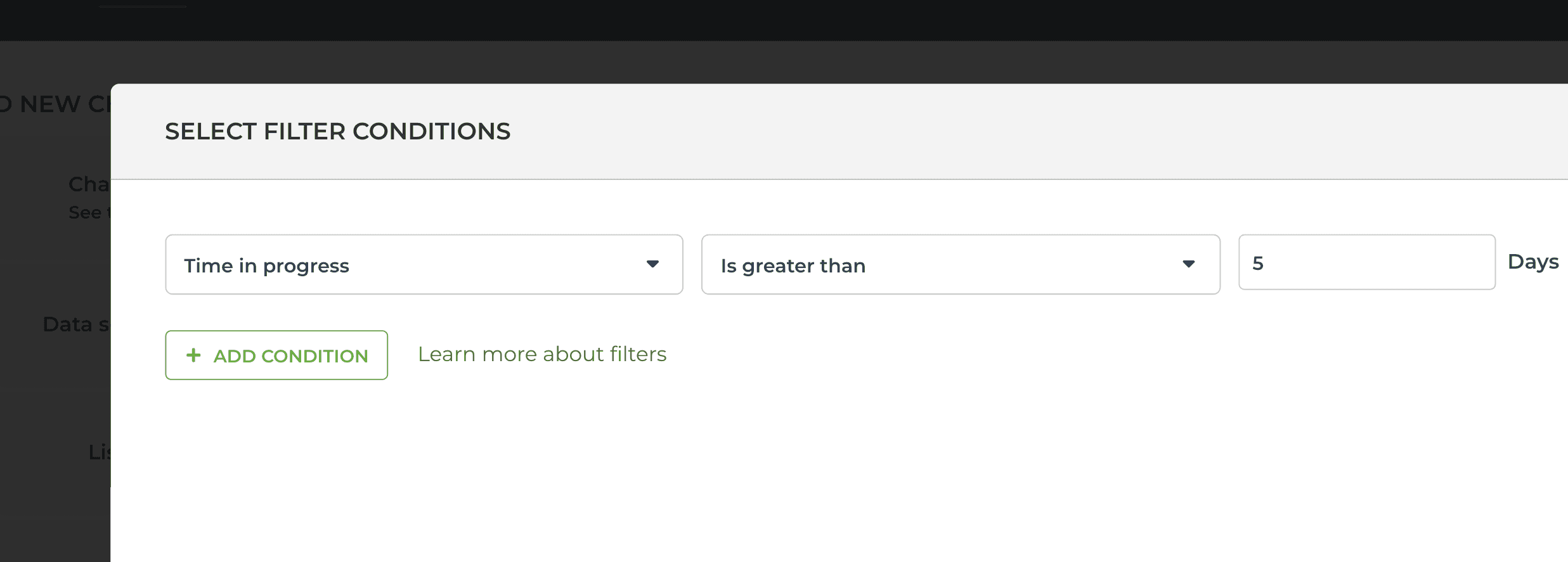
To find items that have been in their current workflow state for longer than a certain number of days, select Time in workflow state:
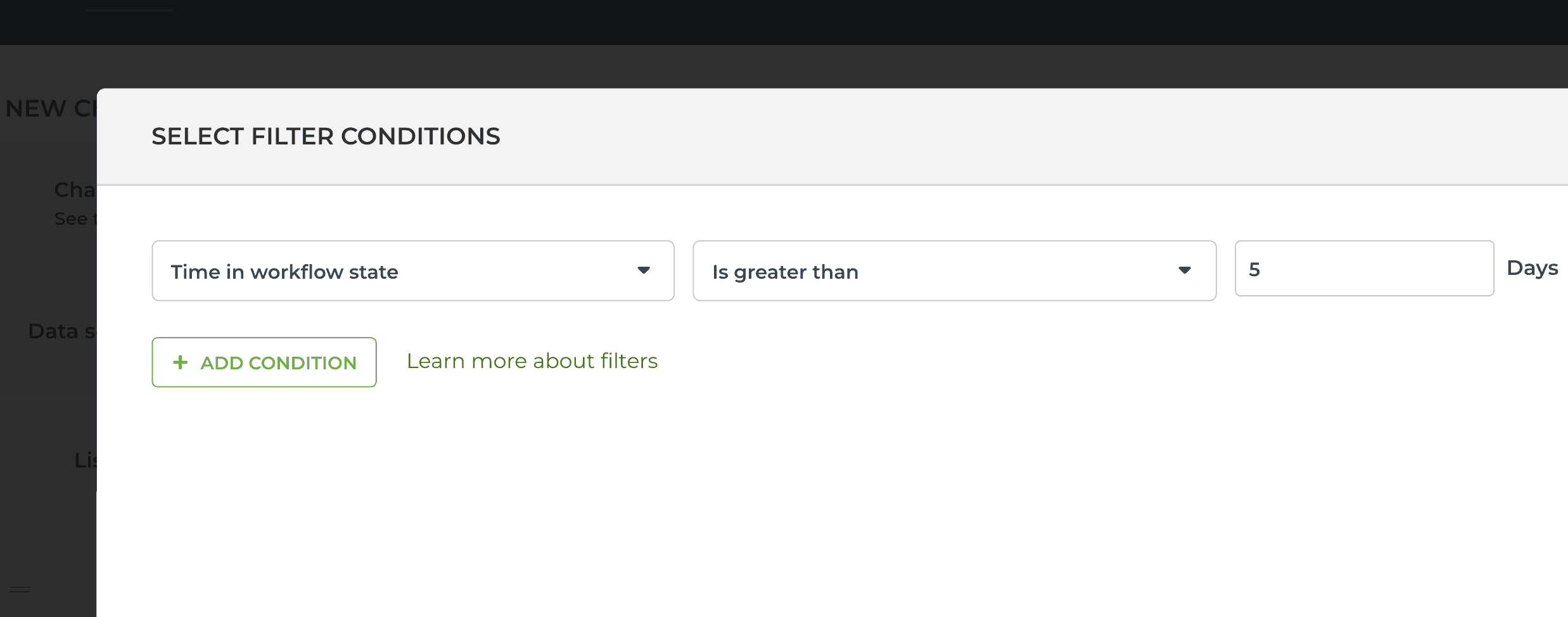
To find items that have spent longer than a certain number of days in a specified workflow state (in the past), you can set a filter like this in the Scatter plot chart:
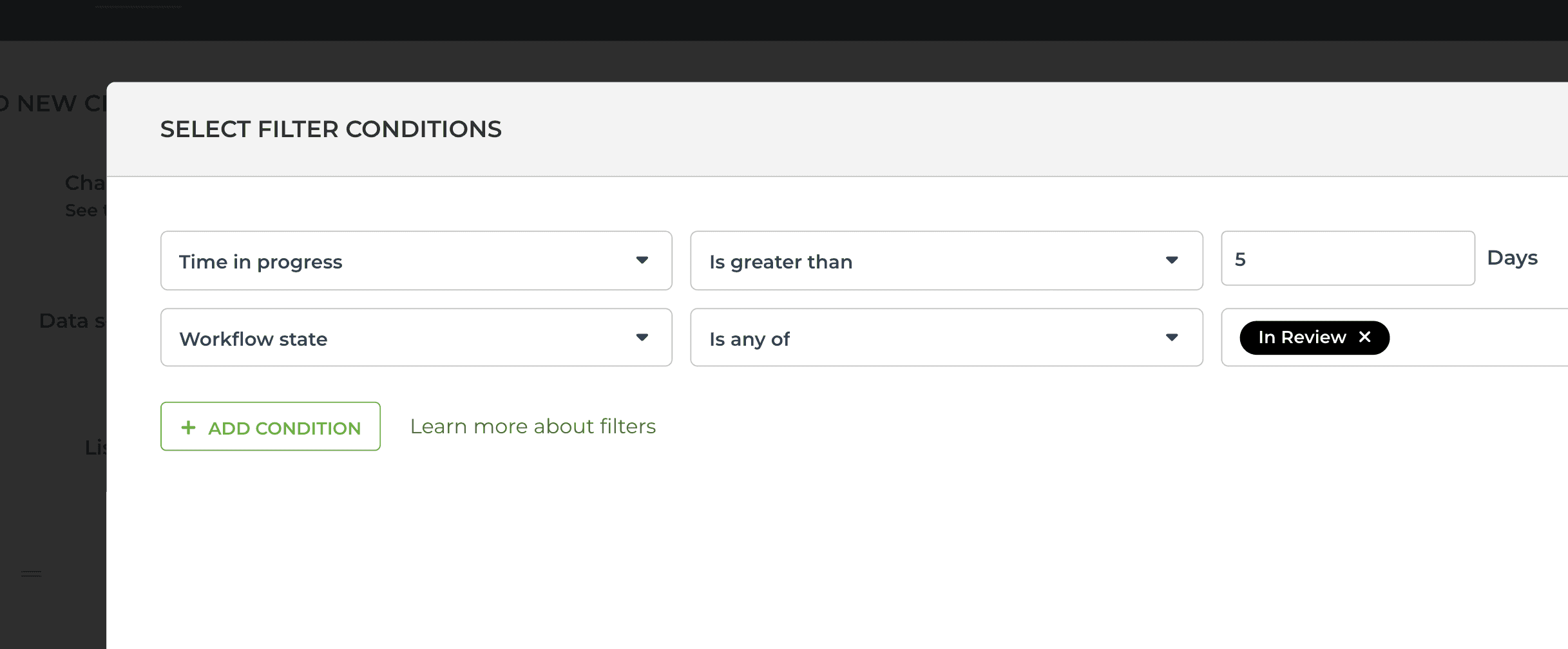
That would include all items that have spent more than 5 days in the In review state.
You can also filter by time logged to time tracking fields:
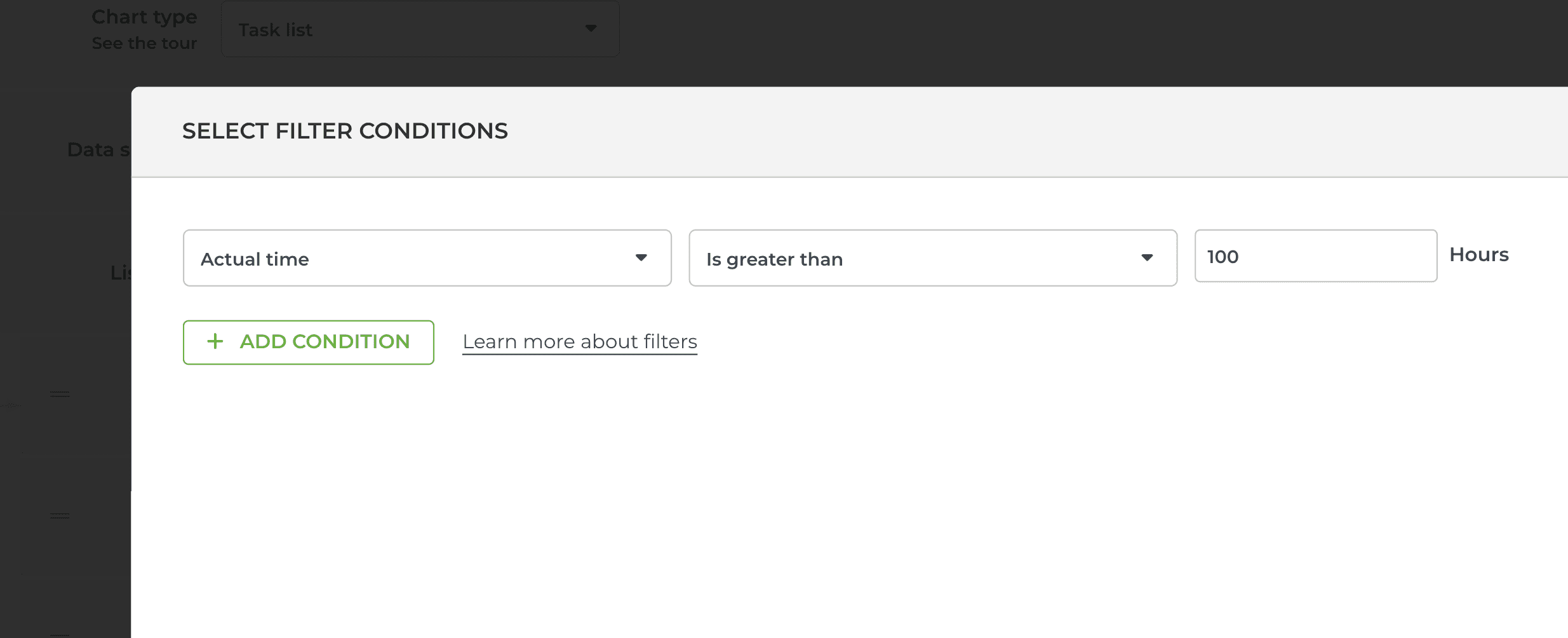
That would include all items with more than 100 hours logged.
Filtering by timings
You can filter by timings such as total time in progress (cycle time), time in a workflow state, or time logged to a time tracking field.
To find items that have been in progress for longer than a certain number of days, select Time in progress from the filter menu:

To find items that have been in their current workflow state for longer than a certain number of days, select Time in workflow state:

To find items that have spent longer than a certain number of days in a specified workflow state (in the past), you can set a filter like this in the Scatter plot chart:

That would include all items that have spent more than 5 days in the In review state.
You can also filter by time logged to time tracking fields:

That would include all items with more than 100 hours logged.
Applying AND/OR logic in filters
The filter logic depends on how you construct the filter conditions. When you select multiple is any of options from a single menu, they follow the OR logic:
“Show me items that match this or that (or both).”
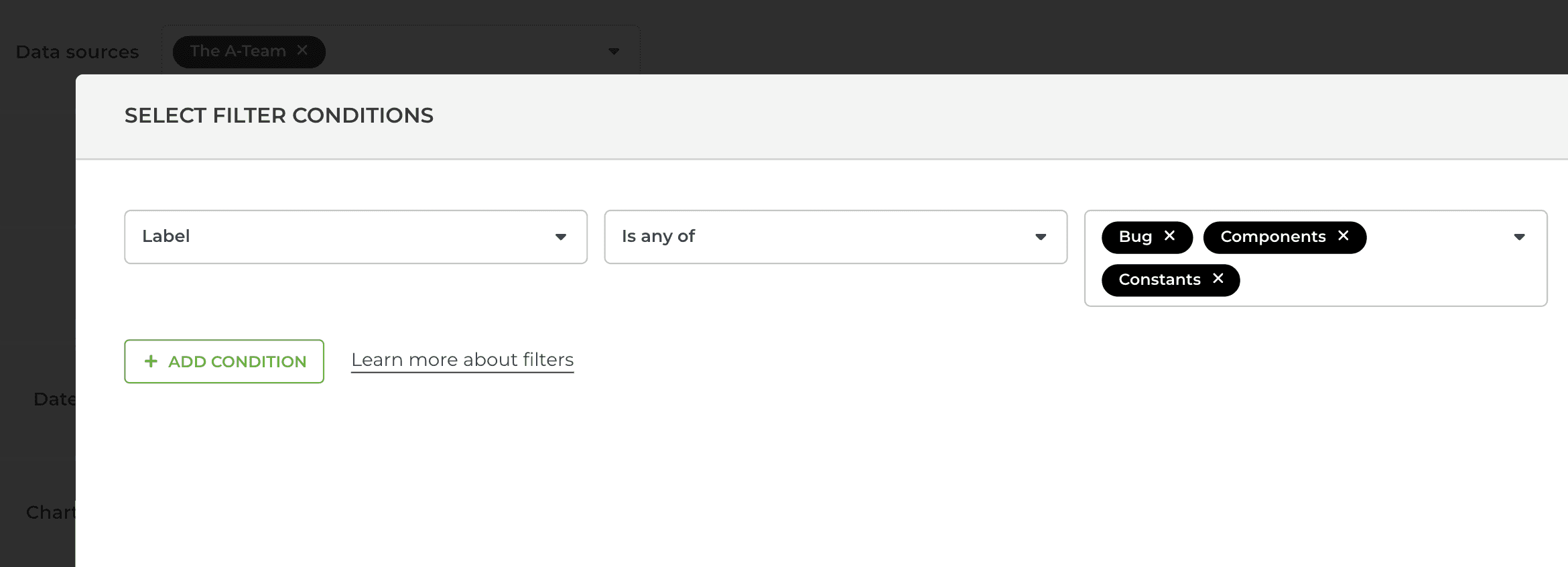
In this case, the filter matches any item that has at least one of the selected options. In terms of logic, they are OR conditions, as it is sufficient if the resulting item contains only one of them.
You can also select multiple options by picking them in separate menus. In terms of logic, they are AND conditions since the resulting items must contain all of them.
“Show me items that match this and that.”
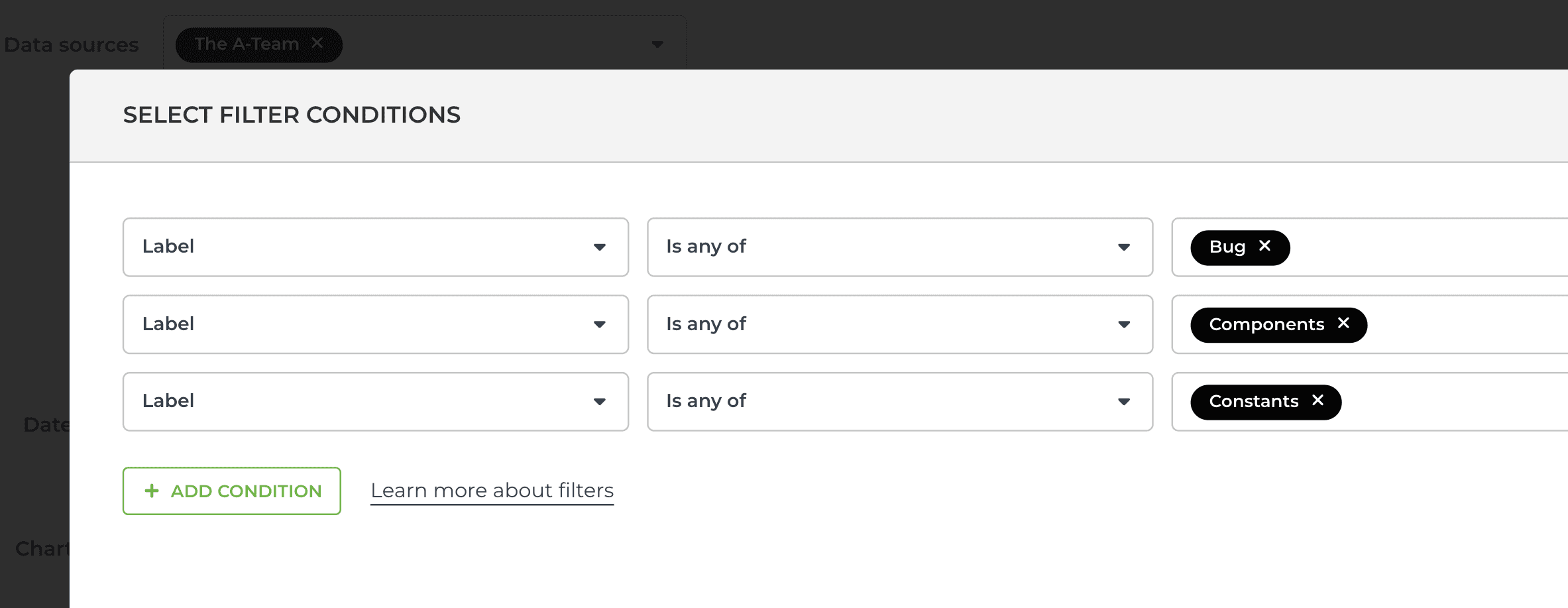
You can combine both in the same filter. Here’s an example of a more complex filter including both AND and OR conditions:
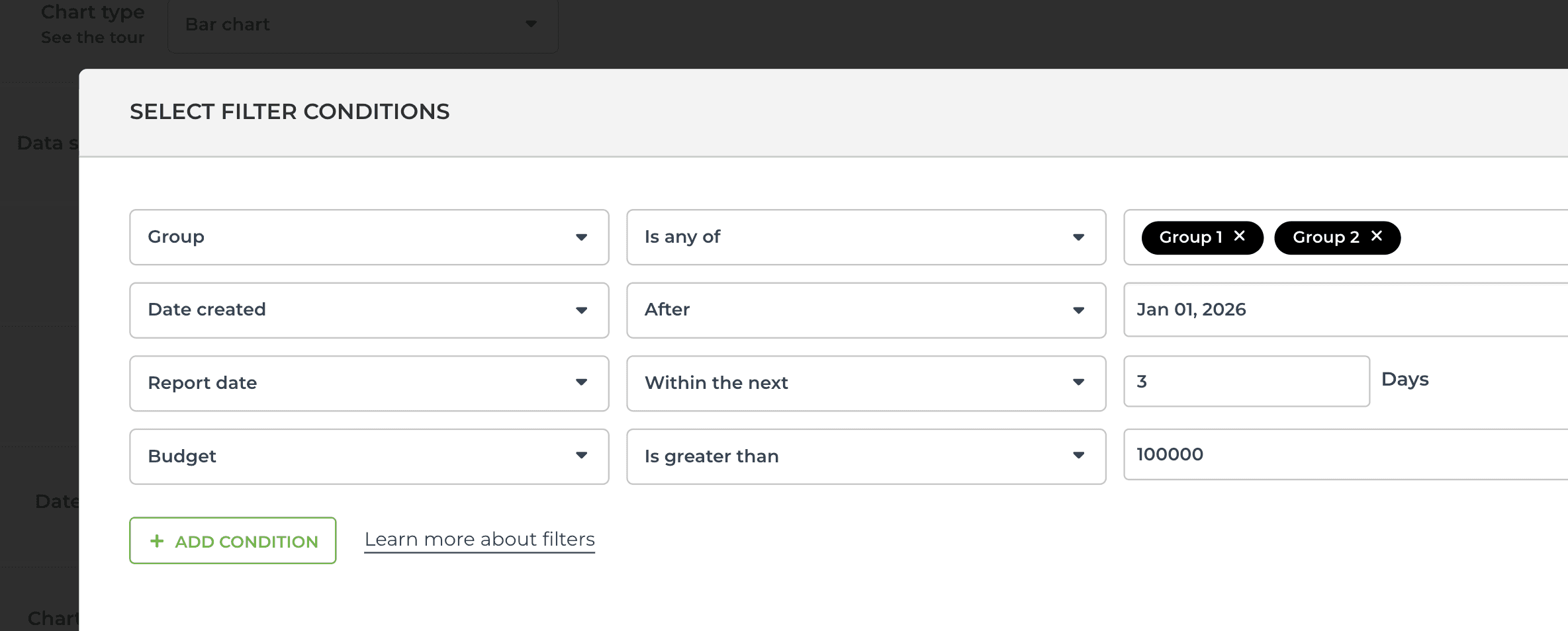
You can add an unlimited number of conditions in one filter, and they can follow either AND/OR logic.
Applying AND/OR logic in filters
The filter logic depends on how you construct the filter conditions. When you select multiple is any of options from a single menu, they follow the OR logic:
“Show me items that match this or that (or both).”

In this case, the filter matches any item that has at least one of the selected options. In terms of logic, they are OR conditions, as it is sufficient if the resulting item contains only one of them.
You can also select multiple options by picking them in separate menus. In terms of logic, they are AND conditions since the resulting items must contain all of them.
“Show me items that match this and that.”

You can combine both in the same filter. Here’s an example of a more complex filter including both AND and OR conditions:

You can add an unlimited number of conditions in one filter, and they can follow either AND/OR logic.
Filtering by overdue, blocked, reopened etc.
To filter a chart by task status, such as blocked, overdue, reopened, completed on time, or completed overdue, select Status from the filter menu and choose the items to include from the following dropdown:
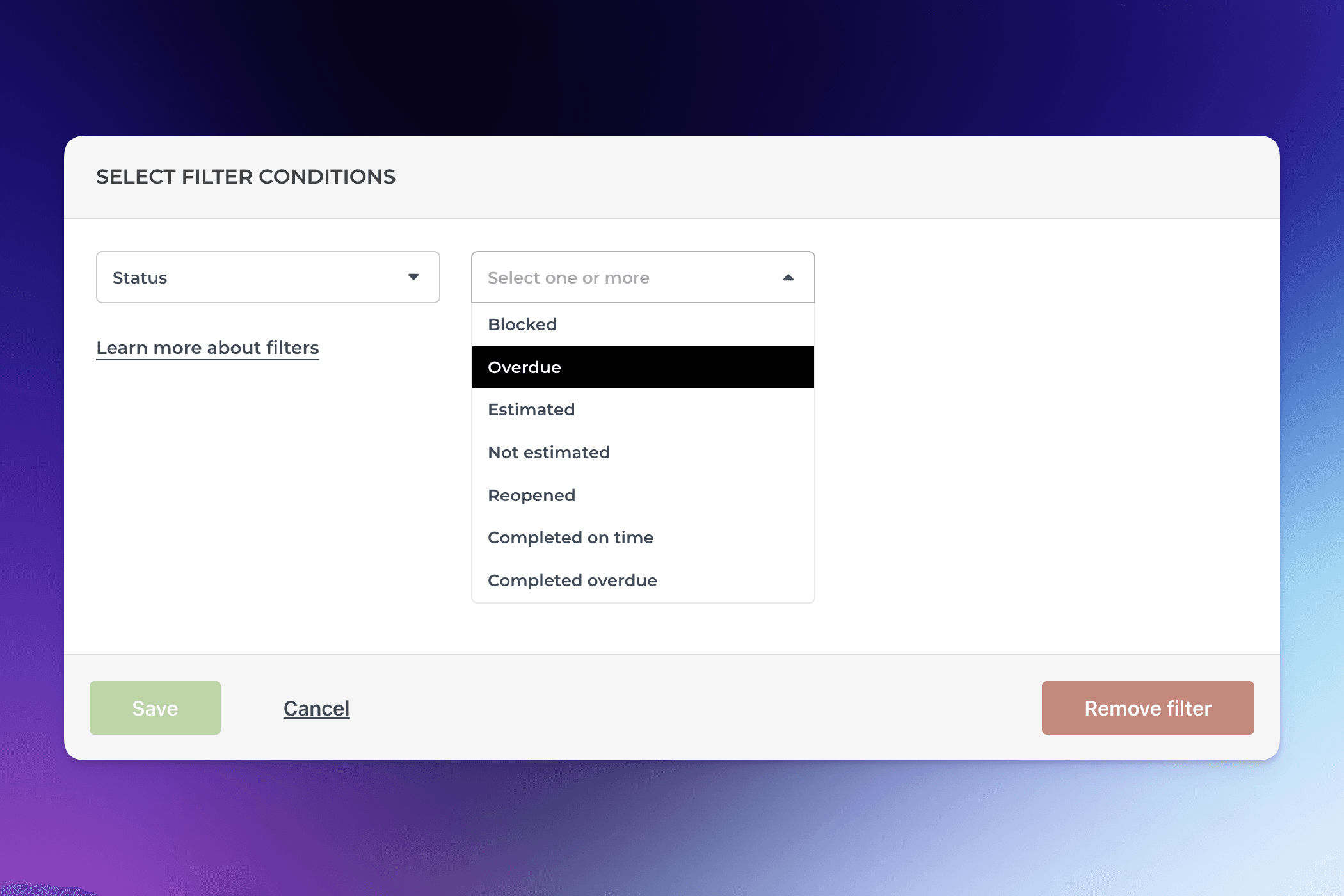
The resulting chart contains the items that meet that criteria.
Filtering by overdue, blocked, reopened etc.
To filter a chart by task status, such as blocked, overdue, reopened, completed on time, or completed overdue, select Status from the filter menu and choose the items to include from the following dropdown:

The resulting chart contains the items that meet that criteria.
Configuring a quick filter
In the chart settings, you can configure a quick filter that will be shown on top of the chart. It allows adjusting the chart's content without accessing the chart editor.
In the chart settings, use the toggle to enable the quick filter:
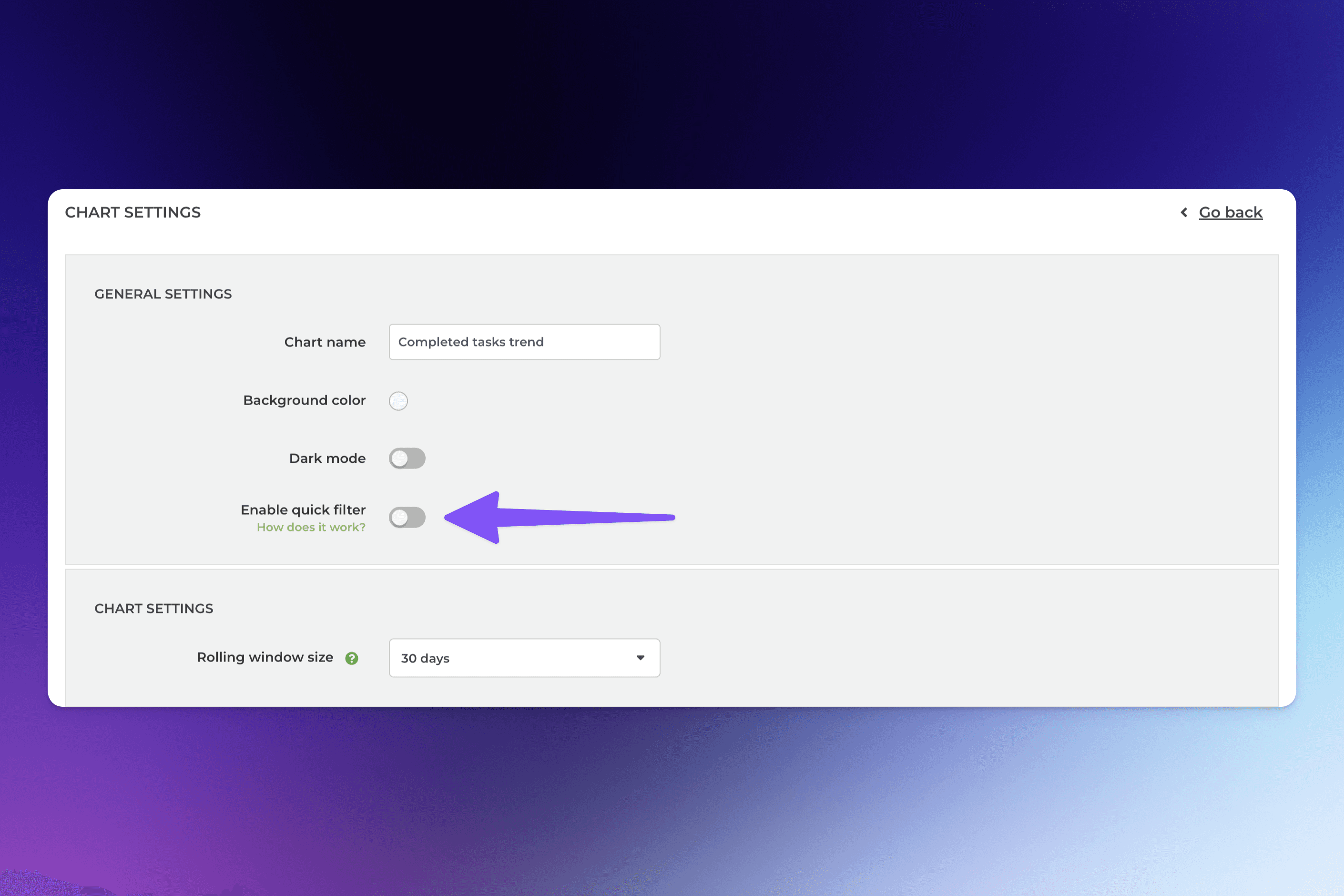
Clicking the toggle reveals the filter options. These are the same options as what you have when setting a filter in the chart editor.
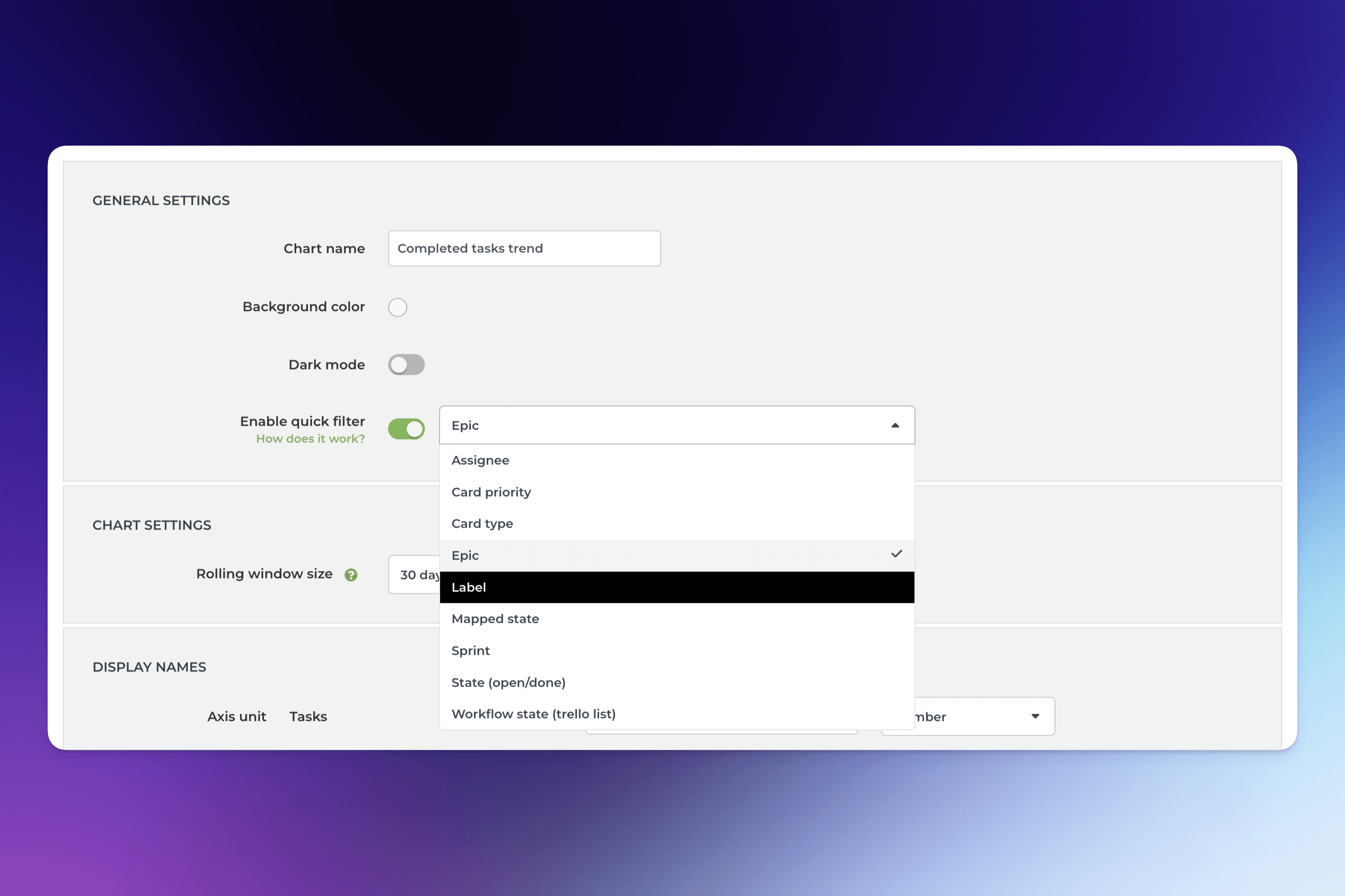
For example, selecting Label from the menu creates a quick filter for the label shown above the chart. The default selection is All labels, and you can filter the content by any available label by picking a label from the menu:
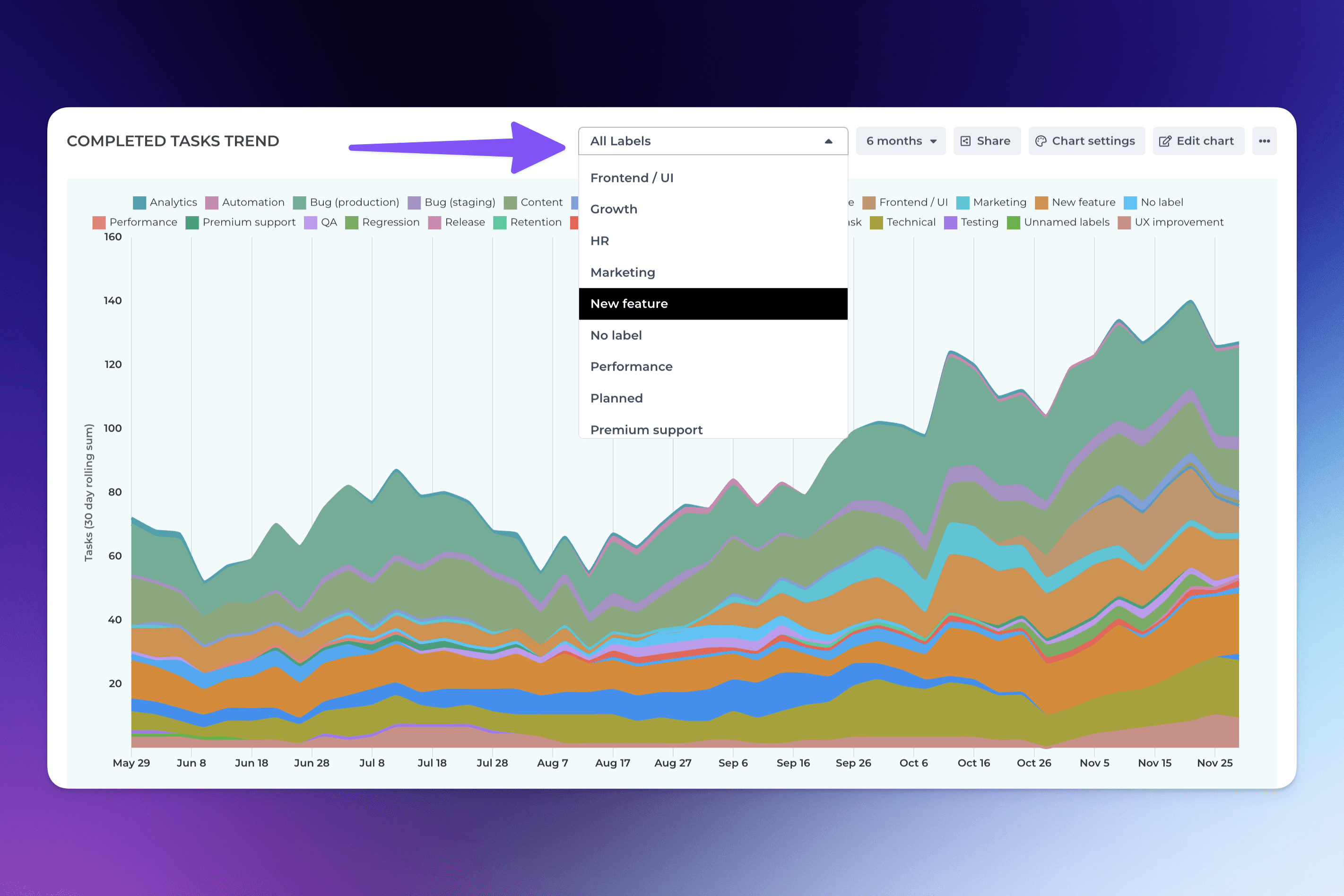
When you select filter criteria from the menu, the chart content is filtered by that selection. It allows quick comparisons between labels, iterations, departments, customers, or any other property you have in your data!
You can limit the number of options in a quick filter by setting the same filter inside the chart editor. The quick filter will contain only the items that are explicitly included in the filter
When you enable a quick filter for a chart, it will be present when the chart is shared with a link, embedded in a website, or added to a report.
Configuring a quick filter
In the chart settings, you can configure a quick filter that will be shown on top of the chart. It allows adjusting the chart's content without accessing the chart editor.
In the chart settings, use the toggle to enable the quick filter:

Clicking the toggle reveals the filter options. These are the same options as what you have when setting a filter in the chart editor.

For example, selecting Label from the menu creates a quick filter for the label shown above the chart. The default selection is All labels, and you can filter the content by any available label by picking a label from the menu:

When you select filter criteria from the menu, the chart content is filtered by that selection. It allows quick comparisons between labels, iterations, departments, customers, or any other property you have in your data!
You can limit the number of options in a quick filter by setting the same filter inside the chart editor. The quick filter will contain only the items that are explicitly included in the filter
When you enable a quick filter for a chart, it will be present when the chart is shared with a link, embedded in a website, or added to a report.
Learn more
Learn more
FAQ
Common questions
A data source is a Linear Team. The pricing is based on the number of teams you explicitly import to Screenful, not the total number of teams in Linear. One data source can contain any number of projects. You can compare plans on the pricing page.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
A data source is a Linear Team. The pricing is based on the number of teams you explicitly import to Screenful, not the total number of teams in Linear. One data source can contain any number of projects. You can compare plans on the pricing page.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Does this support my specific workflow or do I have to use some specific states like "open", "in progress" and "done"?
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
FAQ
Common questions
A data source is a Linear Team. The pricing is based on the number of teams you explicitly import to Screenful, not the total number of teams in Linear. One data source can contain any number of projects. You can compare plans on the pricing page.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
A data source is a Linear Team. The pricing is based on the number of teams you explicitly import to Screenful, not the total number of teams in Linear. One data source can contain any number of projects. You can compare plans on the pricing page.
You can import data sources from all the tools we support in the same Screenful account. Learn more about managing data sources.
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
You can manage the subscription in the billing settings. The location of the billing settings depends on the product you are subscribed to. You can learn more by following the instructions in this guide.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
We do not make changes to your data. We only read it via the API of your tool. Screenful is only for reporting and analytics. It does not update any data within your tools.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
All data sources are synced automatically once per hour. Changing settings or configuration will trigger additional sync so your data is at most one hour old. You can sync data manually at any time in the sync settings.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
Yes, you can create charts with a prompt and ask questions about a chart by using the Screenful AI Assistant. The assistant combines the leading LLMs with advanced multidimensional data analytics to help you understand and interpret your data.
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
What is the difference between these metrics?
Reaction time = time before the work was started
Cycle time = time from start to completion
Lead time = Reaction time + Cycle time
Timing metrics explained: Lead time vs Cycle time
How is the reaction time calculated?
Reaction time starts running when a task is moved into a state that is mapped to the "Not started" in the workflow mapping. The reaction time stops when the task is moved out from that state. If the task is never placed into a state that is mapped to the “Not started” workflow state, then the reaction time is zero.
What if tasks skip lists/columns, or there is no sequential workflow?
The timing information is based on how long items stay in the workflow states that are mapped to "In progress" in the workflow mapping. There is no need for sequential progress, and it is totally fine if tasks skip some of the workflow steps.
What if a task is moved from the “not started” state directly to “done” without going through any of the “in progress” states?
In that case, the cycle time will be zero.
How does the cycle time work if a task is moved into "in progress" and then back to "not started yet"? Similarly, what happens if a card is archived while it's in progress?
Cycle time is calculated only for completed tasks, so in both of those cases, cycle time would be undefined.
If a task is moved from "in progress" to "done", but then back to "in progress" again for additional work would this time be added to the cycle time?
Cycle time is counted only when the task is in progress, so the time spent in the "done" state is not included in the calculation.
When is a task created? Does the clock start when a task is created or when it is put in the "next" state (or equivalent)?
The clock starts when a task is moved to a workflow state that is mapped to the "not started" or "in progress" workflow state.
Are weekends included in the cycle time calculations?
Weekends are included in the calculations by default, but you can change that in the chart settings by selecting 'Exclude non-business hours. See How to set weekend days and office hours
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
By default yes, but you can specify your working hours and days in the Account Settings.
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Yes, there are a few different ways you can filter out outliers from the charts, including
Filtering by item name
Filtering by how long an item has been in progress
Setting a label and filtering out based on that label
You can learn more from this guide: How to remove outliers from data?
Does this support my specific workflow or do I have to use some specific states like "open", "in progress" and "done"?
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You are not limited to any specific set of states or a workflow. You can configure your own workflow, if such exists, and you can use that in your reporting. It's also ok if you don't have any workflow in your boards, as can create reports based on any other criteria by setting a filter.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
You can embed any custom chart or report to any web page using the embed code. Learn more about the sharing feature from the online guide.
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
The Getting Started Guide contains Instructions for setting up Screenful.
See also our Accounts & Pricing FAQ.
Check out our knowledge base and video tutorials, or get in touch by emailing support@screenful.com
Troubleshooting
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.
Troubleshooting
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
While both the public and private channels are shown in the menu, you won’t receive the report to a private channel without explicitly adding the Screenful app to that channel. Learn how to enable sending to a private Slack channel.
There can also be restrictions on who can install apps to your Slack. Learn how to manage app approval in your Slack workspace.
Some browser plugins may interfere with the authorization process. If you see an empty page during the authorization or the list of channels is empty, you should try with another browser (or ask your colleague to do the Slack authorization).
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
Filter options are derived from task data, which means that if you recently added some properties, such as labels, but haven't yet assigned them to any tasks, they won't show up in the filter options. As soon as you assign them to tasks, they will show up in the filter options from then on.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.
If you or your colleague didn't receive the user invitation email, you can go to the user settings and click the Copy invitation link button to copy the link to the clipboard. After that, you can share the link via any channel (email, Slack, Teams, etc). You can learn more from the user invitation guide.